
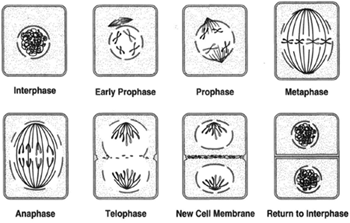
In animal cells, two pairs of centrioles formed from the replication of one pair are located outside of the nucleus.Īt the end of interphase, the cell enters the next phase of meiosis: Prophase I. Mitosis starts when condensed chromosomes become visible in the prophase nucleus.The daughter cells are clones of each other. The nucleus is bounded by a nuclear envelope and the cell's chromosomes have duplicated but are in the form of chromatin. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which a diploid body cell copies itself and finally divides into two identical diploid daughter cells.In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present.Note that the G in G2 represents gap and the 2 represents second, so the G2 phase is the second gap phase. The cell synthesizes proteins and continues to increase in size. Mitosis is conventionally divided into four stagesprophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophasewhich are illustrated for an animal cell in Figures 14.23 and 14.24. Phases of mitosis Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. After going through the S phase, the chromosomes enter prophase where the chromosomes are replicated and have two identical chromatids. G2 phase: The period after DNA synthesis has occurred but prior to the start of prophase. Chromosomes are unreplicated during interphase as represented by the four chromosomes with the D/B, E, d/b, and e genes.In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized. S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized.Note that the G in G1 represents gap and the 1 represents first, so the G1 phase is the first gap phase. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The mitosis cell cycle includes several phases that result in two new diploid daughter cells. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA. The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell cycleinterphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesisto successfully make the new diploid cells.

At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
